
The Emergence of Electronic Identity
In an increasingly digital world, the concept of electronic identity has gained immense significance. Your electronic identity represents your online persona, which is crafted through a combination of various digital attributes, including usernames, passwords, biometric data, and other personal identifiers.
This article will delve into the complexities surrounding electronic identity and explore its implications for security, privacy, and accessibility. To understand this topic better, you can refer to electronic identity https://www.wwpass.com/electronic-identity.
What is Electronic Identity?
Electronic identity, often abbreviated as e-ID, refers to the collection of digital information that uniquely identifies an individual in an online environment. This can range from simple digital credentials like usernames and email addresses to more complex identifiers like digital certificates and biometric data (fingerprints, facial recognition, etc.). An e-ID is crucial for authenticating users in various online transactions, from social media platforms to banking and shopping websites.
The Importance of Electronic Identity
As we navigate through an era where almost every sector is digitizing, the importance of electronic identity becomes painfully clear. Here are some of the main reasons why it matters:
- Security: E-ID serves as a protective barrier that helps verify user identities, reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access. With the rise in cybercrime, having a robust electronic identity framework is crucial for protecting sensitive information.
- Convenience: Electronic identities facilitate quicker and easier access to services. Users can authenticate themselves across different platforms without the repetitive process of creating new accounts.
- Accessibility: E-IDs enable individuals, especially in remote areas, to access services online that were previously unavailable due to geographical constraints.
Forms of Electronic Identity
Electronic identities can take various forms, including:
- Username and Password: The most basic form of e-ID, where users create accounts using a combination of a username and a password.
- Social Media Logins: Utilizing existing social media accounts (like Facebook, Google, or Twitter) to authenticate users across different platforms.
- Biometric Authentication: More sophisticated systems that leverage fingerprint scanners, facial recognition, or voice recognition for secure access.
- Digital Certificates: Issued as part of a public key infrastructure (PKI) to establish the authenticity of users in various online services.
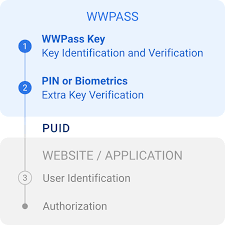
Applications of Electronic Identity
The use of electronic identity spans numerous sectors. Here are a few key applications:
- Banking and Finance: Users can securely log into their accounts and conduct transactions online using their e-ID.
- e-Government Services: Governments are increasingly adopting e-ID systems for providing citizens with online access to their services, such as tax submissions, voting, and healthcare.
- E-commerce: Online shopping platforms leverage e-ID to process transactions efficiently and securely, thus enhancing user experiences.
- E-Learning: Educational institutions can authenticate students, allowing them to access online courses and materials safely.
Challenges of Electronic Identity
Despite the advantages, electronic identity solutions also face significant challenges:
- Privacy Concerns: With increasing amounts of personal data being collected, users worry about how their information is stored, used, and potentially misused.
- Fraud and Cybersecurity: Cybercriminals continuously exploit weaknesses in e-ID systems, leading to identity theft and other forms of fraud.
- Standardization: The lack of universal e-ID standards creates fragmentation, complicating the adoption across different systems and platforms.
- User Awareness: Many individuals remain unaware of the importance of secure e-ID practices and risk exposing themselves to vulnerabilities.
The Future of Electronic Identity
As technology advances, the landscape of electronic identity is poised for transformation. The future may witness:
- Decentralization: Technologies like blockchain might offer decentralized solutions for identity management, enhancing security and user control.
- Increased Use of Biometrics: With improved technology, biometric authentication could become even more common, possibly replacing traditional passwords.
- E-ID Legislation: Governments are likely to introduce regulations that ensure the protection of e-ID and user privacy, establishing framework guidelines.
- User-Centric Designs: Solutions that enhance user experiences through intuitive interfaces and minimized friction will become central to e-ID development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electronic identity is an integral component of our digital lives, enabling secure access to various online services while also presenting challenges that demand attention. The evolution of e-ID systems will shape the future of digital interactions, blending convenience with the imperative of security and privacy. As we adopt these technologies, awareness and education will be key in navigating the complexities of electronic identity, ensuring that individual identities remain protected in the digital age.


